If you can see this check that
| next section | prev section | up | prev page | next page |
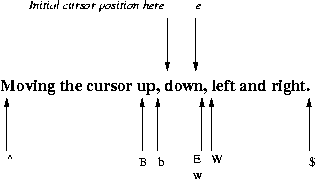
As well as using the keys h,j,k, and l to move the cursor left, down, up, and right respectively, must terminals let you use the arrow keys to perform the same function.
Another useful cursor moving command is G, which functions as a goto command. For example, to go to line 256 of a file you would type 256G and the cursor would move to that line. To find out your current line number at any time, you can press CTRL-G in command mode and to display the line numbers along the left margin of your file, you can type
:set number

| Centos 7 intro: | Paths | BasicShell | Search |
| Linux tutorials: | intro1 intro2 wildcard permission pipe vi essential admin net SELinux1 SELinux2 fwall DNS diag Apache1 Apache2 log Mail |
| Caine 10.0: | Essentials | Basic | Search | Acquisition | SysIntro | grep | MBR | GPT | FAT | NTFS | FRMeta | FRTools | Browser | Mock Exam | |
| Caine 13.0: | Essentials | Basic | Search | |
| CPD: | Cygwin | Paths | Files and head/tail | Find and regex | Sort | Log Analysis |
| Kali 2020-4: | 1a | 1b | 1c | 2 | 3 | 4a | 4b | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8a | 8b | 9 | 10 | |
| Kali 2024-4: | 1a | 1b | 1c | 2 | 3 | 4a | 4b | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8a | 8b | 9 | 10 | |
| Useful: | Quiz | Privacy Policy | Terms and Conditions |
Linuxzoo created by Gordon Russell.
@ Copyright 2004-2025 Edinburgh Napier University