If you can see this check that
| next section | prev section | up | prev page | next page |
> telnet localhost > telnet 127.0.0.1 > ping localhost
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:16436 Metric:1
RX packets:10 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:10 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:700 (700.0 b) TX bytes:700 (700.0 b)
In many systems /dev/eth* is the naming convention used for ethernet network devices. In such systems with only one network connection, /dev/eth0 is the standard device name. However some distributions are renaming eth0 to reflect the hardware bus number of the network device in question.
Naming devices to reflect their hardware identity (such as using the PCI slot number) means that the names better reflect the location of the device, and also gives a degree of protection from the effects of hardware changes.
In systems like Fedora, eth0 is more likely to be known as /dev/em1. This suggests the device is in slot 1, and is an embedded ethernet device (i.e. on the motherboard).
When configuring a network interface, the basic network configuration requires:10.0.1.20/24
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr FE:FD:0A:00:02:02
inet addr:10.0.2.2 Bcast:10.0.2.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::fcfd:aff:fe00:202/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:2008 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:1181 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:106268 (103.7 Kb) TX bytes:166284 (162.3 Kb)
Interrupt:5
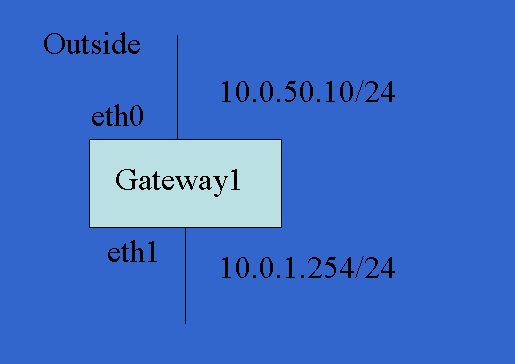
ifconfig eth0 10.0.50.10 broadcast 10.0.50.255
netmask 255.255.255.0
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP> mtu 16436 qdisc noqueue
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast qlen 1000
link/ether 00:a0:24:e1:29:4e brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 146.176.162.6/24 brd 146.176.162.255 scope global eth0
inet6 fe80::2a0:24ff:fee1:294e/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
0: from all lookup local 32766: from all lookup main 32767: from all lookup default
broadcast 127.255.255.255 dev lo proto kernel scope link src 127.0.0.1 broadcast 10.0.2.0 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 10.0.2.2 local 10.0.2.2 dev eth0 proto kernel scope host src 10.0.2.2 broadcast 10.0.2.255 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 10.0.2.2 broadcast 127.0.0.0 dev lo proto kernel scope link src 127.0.0.1 local 127.0.0.1 dev lo proto kernel scope host src 127.0.0.1 local 127.0.0.0/8 dev lo proto kernel scope host src 127.0.0.1
10.0.2.0/29 dev eth0 scope link src 10.0.2.1 default via 10.0.2.7 dev eth0 > route -n Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface 10.0.2.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.248 UH 0 0 0 eth0 0.0.0.0 10.0.2.7 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
$ ifconfig eth0 10.0.50.10 broadcast 10.0.50.255
netmask 255.255.255.0
$ ip route append 10.0.50.10 dev eth0 table main
$ ip route append default via 10.0.50.254
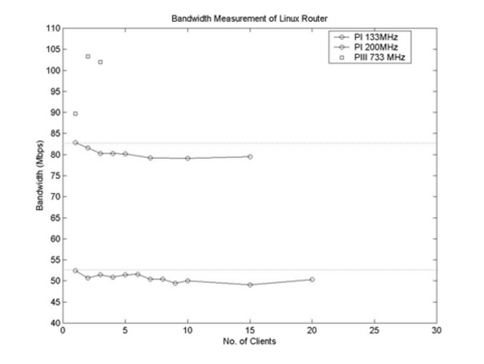
 Ref: http://www.linuxjournal.com/node/5826/print
Ref: http://www.linuxjournal.com/node/5826/print
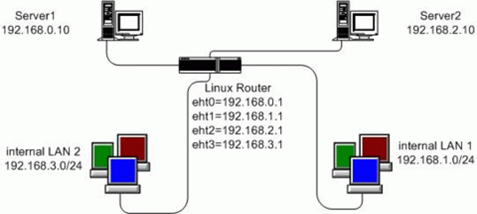
> ifconfig eth0 10.0.50.10 broadcast 10.0.50.255 netmask 255.255.255.0 > ip route append 10.0.50.0/24 dev eth0 > ifconfig eth1 10.0.1.254 broadcast 10.0.1.255 netmask 255.255.255.0 > ip route append 10.0.1.0/24 dev eth1 > ip route append default via 10.0.50.254
10.0.50.0/24 dev eth0 scope link 10.0.1.0/24 dev eth1 scope link default via 10.0.50.254 dev eth0
> ip route show table main 10.0.1.254 dev eth0 scope link default via 10.0.1.254 dev eth0
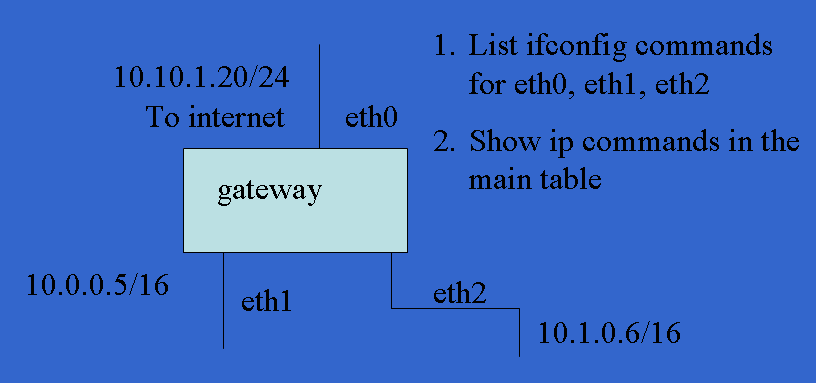
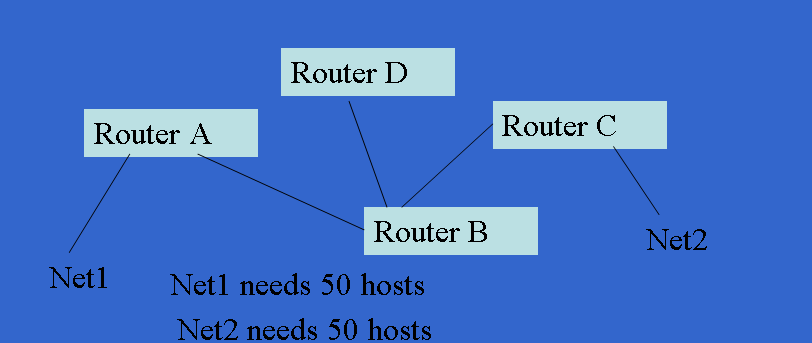
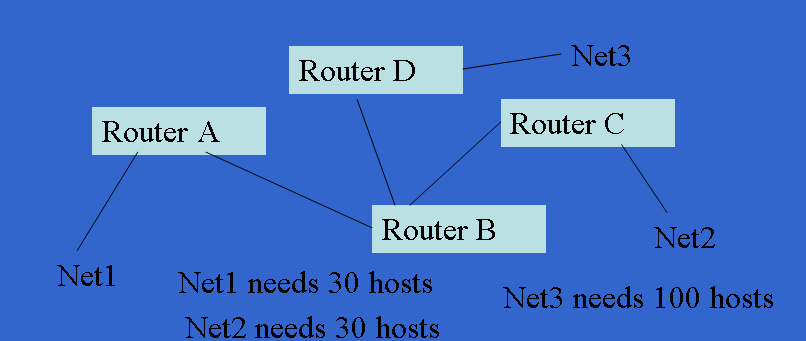
# ************ Create a bridge interface and it is called br1 brctl addbr br1 # ************ Add physical interfaces to the bridge interface brctl addif br1 eth0 brctl addif br1 eth1 # ************ Reset IP interface ifconfig eth0 0.0.0.0 ifconfig eth1 0.0.0.0 #Bring up the bridge ifconfig br1 up # ********** Set IP address of the bridge ifconfig br1 192.168.1.10 netmask 255.255.255.0 up # ********** Set IP default gateway route add default gw 192.168.10.1
> cat /proc/net/arp IP address ... HW address .. Device 146.176.166.254 00:08:7c:6e:90:00 eth0 146.176.166.2 00:e0:81:26:31:06 eth0 > ping 146.176.166.6 > cat /proc/net/arp IP address ... HW address .. Device 146.176.166.254 00:08:7c:6e:90:00 eth0 146.176.166.2 00:e0:81:26:31:06 eth0 146.176.166.6 00:e0:81:25:c7:35 eth0
IP address ... HW address .. Device 146.176.166.254 00:08:7c:6e:90:00 eth0 146.176.166.2 00:e0:81:26:31:06 eth0 146.176.166.3 00:e0:81:26:31:06 eth0
$ nmap linuxzoo.net PORT STATE SERVICE 22/tcp open ssh 23/tcp open telnet 53/tcp open domain 80/tcp open http 81/tcp open host2-ns 123/tcp closed ntp 5900/tcp closed vnc 5901/tcp closed vnc-1 5902/tcp closed vnc-2 5903/tcp closed vnc-3
$ netstat -al | grep LISTEN | grep tcp tcp 0 0 *:http *:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 *:ssh *:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 *:https *:* LISTEN
$ netstat -n | head -4 Active Internet connections (w/o servers) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State tcp 1 0 127.0.0.1:64359 127.0.0.1:631 CLOSE_WAIT tcp 0 0 146.176.162.6:22 146.176.16:59160 ESTABLISHED Not sure about port ":22"? $ grep '22/tcp' /etc/services ssh 22/tcp # SSH Remote Login Protocol bpjava-msvc 13722/tcp # BP Java MSVC Protocol
123/tcp closed ntpWhat is your opinion of the problem?
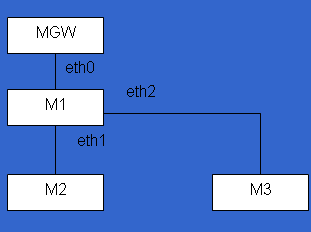
Consider the topology shown
The Ethernet devices shown are from the point of view of M1. Assume MGW is the gateway machine for this cluster of machines. Also from the viewpoint of M1, the following is known:
Eth0 : 162.2.1.20/16 Eth1 : 162.1.1.3/24 Eth2 : 162.1.2.5/24 MGW is 162.2.1.1 M2 is 162.1.1.4 M3 is 162.1.2.10Supply ifconfig lines for this scenario for use on M1.

Eth0 : 162.2.1.20/16 Eth1 : 162.1.1.3/24 Eth2 : 162.1.2.5/24 MGW is 162.2.1.1 M2 is 162.1.1.4 M3 is 162.1.2.10
| Centos 7 intro: | Paths | BasicShell | Search |
| Linux tutorials: | intro1 intro2 wildcard permission pipe vi essential admin net SELinux1 SELinux2 fwall DNS diag Apache1 Apache2 log Mail |
| Caine 10.0: | Essentials | Basic | Search | Acquisition | SysIntro | grep | MBR | GPT | FAT | NTFS | FRMeta | FRTools | Browser | Mock Exam | |
| Caine 13.0: | Essentials | Basic | Search | |
| CPD: | Cygwin | Paths | Files and head/tail | Find and regex | Sort | Log Analysis |
| Kali 2020-4: | 1a | 1b | 1c | 2 | 3 | 4a | 4b | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8a | 8b | 9 | 10 | |
| Kali 2024-4: | 1a | 1b | 1c | 2 | 3 | 4a | 4b | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8a | 8b | 9 | 10 | |
| Useful: | Quiz | Privacy Policy | Terms and Conditions |
Linuxzoo created by Gordon Russell.
@ Copyright 2004-2025 Edinburgh Napier University